算法学习:(单)链表问题
目录
一 链表倒置
链表倒置是链表的基本操作之一。
题目 一 Reverse Linked List
LeetCode 206 Reverse Linked List
Reverse a singly linked list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
Follow up:
A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
题目提示可以用 迭代 或 递归 两种方法来解。
- 迭代方法
如图: 两个指针
两个指针 headp分别指向 表头,欲倒置的元素. 为了使下一个欲倒置的元素不会 野 掉, 还需要一个指针tmp来保护它- p->next 指向 head
- head->next 指向 tmp
- head = p, p = tmp, tmp 保护下一个欲倒置的元素
代码:
12345678910111213141516171819202122class Solution {public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(!head) return NULL;if(!head->next) return head;ListNode *p,*tmp;p = head->next;tmp = p->next;head->next = NULL;while(p1){p->next = head;head = p;p = tmp;if(tmp)tmp = tmp->next;}return head;}};
- 递归方法
思想和上面一样,只不过代码的写法不同:12345678910111213class Solution {public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(!head || !head->next){return head;}ListNode* p = reverseList(head->next);head->next->next = head;head->next = NULL;return p;}};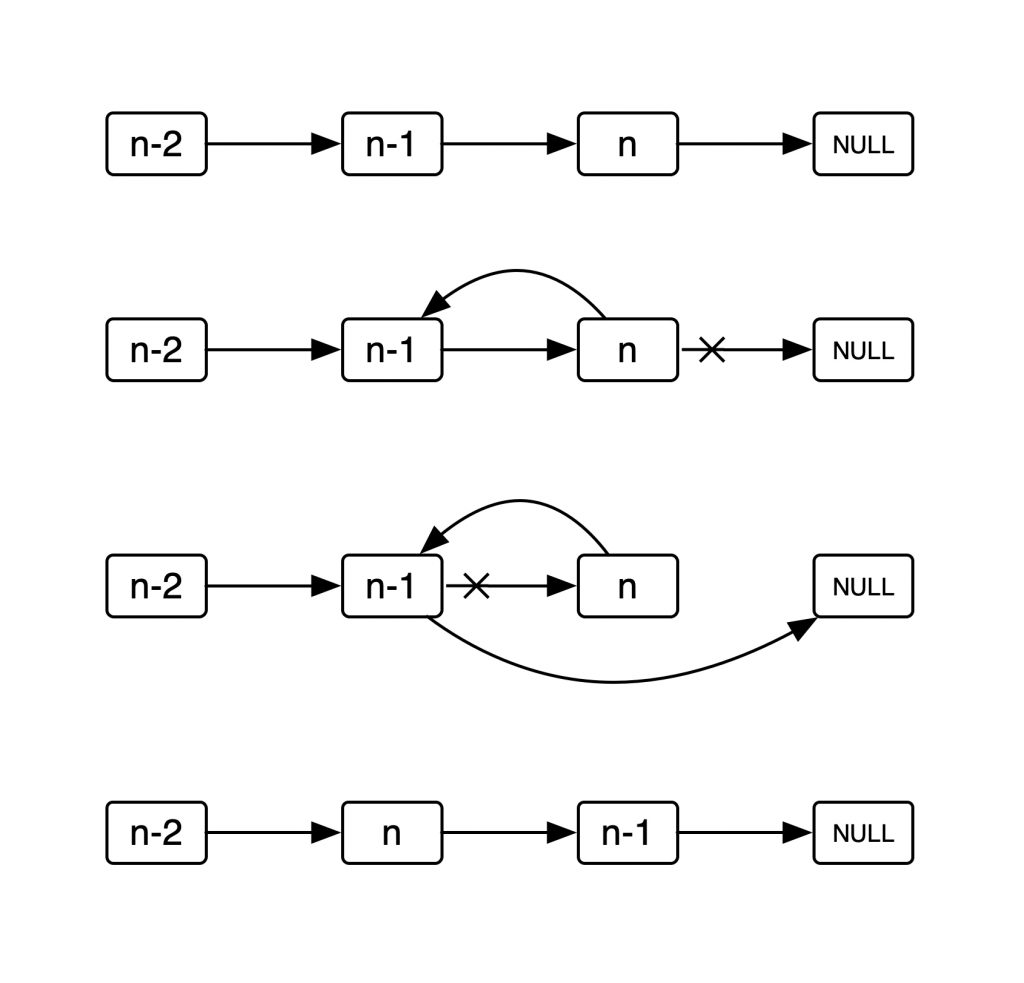
递归的方法代码简洁高效,在很多链表题目中都会用到它,所以特别重要。例如下一题
题目二 Reverse Linked List II
LeetCode 92. Reverse Linked List II
Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in one-pass.
Note: 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ length of list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
Output: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
这一题和上一题没什么不同,不同的只是这题要求在某个区间内倒置。保护好区间前后的元素,不让其野掉,将区间内的元素倒置后再恢复区间前后的指针即可:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
class Solution { public: ListNode* reList(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail){ if(head == tail || head->next == tail) return head; ListNode* p = reList(head->next,tail); head->next->next = head; head->next = tail; return p; } ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) { if(m == n) return head; ListNode* h = head,*p1=head, *t=head; for(int i = 0;i<n;++i){ t = t->next; } if(m == 1) return reList(head, t); p1 = p1->next; for(int i = 0;i<m-2;++i){ p1 = p1->next; h = h->next; } h->next = reList(p1, t); return head; } }; |
其它变形:
- 234. Palindrome Linked List 判断回文链表: 找到链表的中点,将其一半倒置,再比较元素是否相同即可。也许使用栈等容器来解会现快一些,但会增加空间复杂度。
- 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs 成对的倒置。比区间倒置略简单,保护好倒置前后的元素指针即可。
- 25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group 同上题。
- 待添加
二 快慢指针
题目一:Middle of the Linked List
LeetCode 876. Middle of the Linked List
Given a non-empty, singly linked list with head node head, return a middle node of linked list.
If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: Node 3 from this list (Serialization: [3,4,5])
The returned node has value 3. (The judge's serialization of this node is [3,4,5]).
Note that we returned a ListNode object ans, such that:
ans.val = 3, ans.next.val = 4, ans.next.next.val = 5, and ans.next.next.next = NULL.
Example 2:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: Node 4 from this list (Serialization: [4,5,6])
Since the list has two middle nodes with values 3 and 4, we return the second one.
获取链表的中点。可以选遍历链表算出长度,再算出中点,但这样比较麻烦。一个常用的技巧是快慢指针:两个指针都从 head 开始向后挪动,快指针挪动的速度是慢指针的两倍,当快指针挪动到 tail 时,慢指针刚好在链表的中间位置。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
class Solution { public: ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) { if(!head || !head->next) return head; ListNode *s,*f; s = f = head; while(1){ if(!f || !f->next) return s; f = f->next->next; s = s->next; } return s; } }; |
这个技巧在很多题中都会用到。如:
- 234. Palindrome Linked List 判断回文链表: 找到链表的中点,将其一半倒置,再比较元素是否相同即可。也许使用栈等容器来解会现快一些,但会增加空间复杂度。
- 待添加
题目二 141. Linked List Cycle
LeetCode 141. Linked List Cycle
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
题目给出一个链表 ,链表的 tail 节点的 next 会指向 pos 所在的节点。判断出这个链表中是否存在环。解法一:使用哈希表,一旦某个元素被重复访问,即说明存在环。这只该解法空间复杂度为 O(n); 解法二:快慢指针法。如果存在环,则快指针可以追上慢指针。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { if(!head || !head->next) return false; ListNode *s,*f; s = f = head; while(1){ if(!f || !f->next) return false; f = f->next->next; s = s->next; if(s == f) return true; } return false; } }; |
如果存在环,思考一下扩展问题:
- 环中有多少个节点
- 环首在什么位置
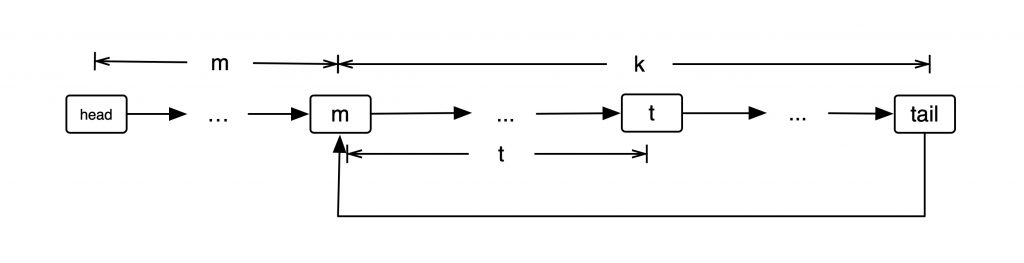
假设环首位于 $m$ 处,环有 $k$ 个结点。快慢指针相遇在 $m+t$ 处,即此时慢指针走过的节点数这 $m+t$ ,那么快指针走过的节点数为 $2m+2t$ 。若此时快指针不动,慢指针要再走一个环的节点数,才能再次与快指针相遇,即 $m+t+k = 2m + 2t$ 。得到 $k = m+t$
题目三: 142. Linked List Cycle II
LeetCode 142. Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
由前面的分析得知:当快慢指针相遇后,慢指针再走 $k-t$ 个结点将到达环首 $m$ .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
class Solution { public: ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { if(!head || !head->next) return NULL; ListNode *s,*f; s = f = head; while(true){ if(!f || !f->next) return NULL; f = f->next->next; s = s->next; if(s == f){ while(true){ if(s == head) return head; s = s->next; head = head->next; } } } } }; |
小节
链表的数据结构简单,熟悉了链表基本操作,解决链表问题也就比较容易了,链表问题的精华就是指针的操作。对于链表的增删操作,注意保护好操作区间前后的节点。对于查找问题,则要了解一些基本的 "套路"